Hyparrhenia hirta
Family: Poaceae
Type of weed: Grass
Flower colour(s): Grey-white
Priority Weed Local Priority Weed. (See more weeds of the Local Priority Weed class.)
Flowering Months: January, February, March, November, December
Description
Coolatai grass is a tufted perennial, forming clumps to 1.5 m tall with tough, dense bases sprouting from rhizomes (root masses).
The leaves are a greyish-green colour turning orangey-red in winter, particularly after frost.
The flowerhead is long and much branched with grey-white, hairy flowers along a stalk. Coolatai grass mainly grows and flowers during late spring to autumn, depending on adequate moisture being available. It grows rapidly after summer rains and if the winter is relatively mild the plant may be green all year.
Plants may produce seed in their first growth season but it is produced over an extended period and shed as it matures.
Alert:
Coolatai grass can be confused with Kangaroo Grass (Themeda australis), Barbed-Wire Grass (Cymbopogon refractus) and some native spear grasses.
Dispersal
The tiny seeds are spread by the wind, by adhering to clothing, animals, vehicles and tools, especially when wet. Human activities such as slashing or traffic assist in spreading the weed, especially along roadsides. It spreads along drainage lines, indicating that water can also transport seeds.
Impact on bushland
Coolati Grass forms clumps that cause displacement of native plants. It also replaces vegetation along drainage lines.
Distribution
Lower Blue Mountains, Upper Blue Mountains. Blackheath, Woodford, Linden, Faulconbridge and Hazelbrook (incursions are occurring in new areas).
Alternative planting
Native plants
- Kangaroo Grass (Themeda australis)
- Barbed-Wire Grass (Cymbopogon refractus)
Council provides a tool, on its Mountain Landscapes website, to help you choose native alternative plantings. Choose your village, soil, vegetation community and the purpose of your planting, and the tool will give you suggestions.
There are native nurseries in several Blue Mountains villages, including Glenbrook, Lawson and Katoomba. Please also ask at your favourite local nursery.
Control
- Remove flowers, fruit, pods or seeds
- Crown
- Spray
Manual control
Crowning
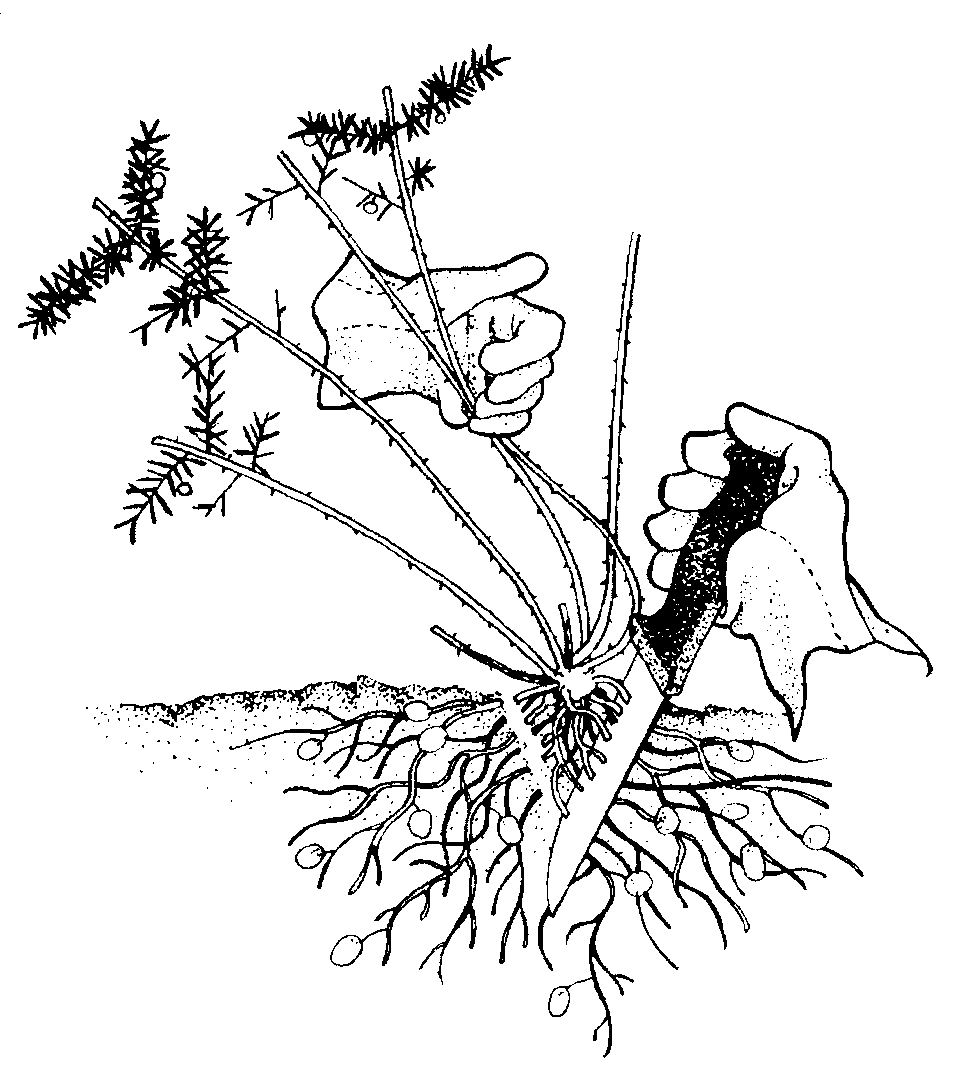
Gently remove and bag seeds or fruit. Push a narrow trowel or knife into the ground next to the tap root. Carefully loosen soil. Repeat this step around the tap root. Grasp stem at ground level, rock plant backwards and forwards and pull gently. Softly tap the roots to dislodge soil. Replace disturbed soil and pat down lightly.
Remove seeds, pods or fruit
Gently remove any seeds, pods or fruit and carefully place in a bag.
Chemical control
Note: Herbicides that may be used for this weed include Glyphosate.
Spraying
Please consult the Herbicide page of this website to help you decide whether to spray, how to do it safely and more.
Specific control tips for this weed
For small infestations, single plants and small patches can be controlled by hand removal, by cutting through the fibrous roots (crowning). Use a knife in a circular action just below the crown. Physical removal is the preferred method as it is difficult to identify when seed production commences and because the plant is found in small infestations.
Spot spray with herbicide. Larger areas can be treated with a selective herbicide registered for use on the specific grass weed.
All flowering and seeding material should be bagged and disposed of appropriately.
Follow-up is required.
For key points on these techniques:
Local Priority Weed
Control measures:
- The plant should be fully and continuously suppressed and destroyed.
- Plants under 4 metres in height should be fully and continuously suppressed and destroyed.
- The spread of this plant should be adequately contained to prevent spread impacting on priority assets. Weed notices will only be issued for these weeds under special circumstances.


